
Comprehensive overview of all railing regulations: from minimum height to opening dimensions and detailed handrail requirements.
See how fast it worksFrom a fall height of 1000 mm, a railing is always required. Period.
The measurement is taken vertically from the top edge of the railing (usually identical with the handrail) down to an imaginary line connecting the step nosings. In practice, railing height is measured directly above the step nosing.
Important: On winder stairs, the railing line would be curved. For easier fabrication – and because some do not like curved railings – a straight railing is often installed. In that case, the minimum height must still be observed!
In general buildings according to DIN 18065, where the presence of children can be expected, no openings larger than 120 mm are permitted in railings. This applies, for example, to the spacing between balusters.
These railings must also prevent children from climbing, either by construction up to a height of 700 mm or by recessing the handrail 150 mm inward.
In practice, it is difficult to define where the presence of children must be expected. On an open day, this may also apply in a workshop.
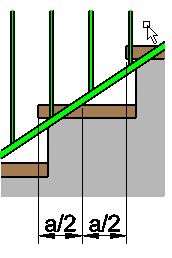
The lateral distance from step/landing to the railing must not exceed 60 mm.
For general buildings under DIN 18065, additional requirements apply:
From the side view, the bottom edge of the railing must be no more than 60 mm above the landing surface. Furthermore, the bottom edge must cover at least half the tread depth.
The distance of the railing in the areas below the treads must be at least 20 mm to avoid finger entrapment.
For general buildings, only the following special rules apply:
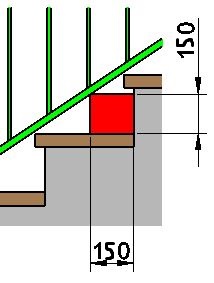
The underside of the railing must be arranged so that a 150 mm cube cannot pass through in any orientation from the step side.
At landings, the maximum gap to the underside of the railing is 120 mm.
Note: Some state building codes differ, e.g., in Bavaria the gap must not allow a beer bottle to roll through.
Stairs must have at least one handrail. Its top must be between 800 and 1150 mm above the stair. Usually the railing top doubles as a handrail, but strictly speaking, they are independent elements.
The handrail width should be 25 to 60 mm, with a grip-friendly profile.
To prevent hand entrapment, the lateral distance to other building parts (e.g., walls) must be at least 50 mm.
Newer and somewhat complex are the rules on interrupted handrails. In general buildings, handrails must be continuous.
In other buildings, the handrail may be interrupted at corners. The background is that winder stairs often use straight handrails, which always represent a compromise in height and do not meet evenly in corners. The clear gap between the ends must be 50–200 mm, the height offset must not exceed 200 mm, and the rising handrail must never end above the start of the next section.
In accessible building design, handrails are a key topic — see link.
Round handrails with a 45 mm diameter are the most widely supported in terms of accessories and are popular for aesthetic reasons. However, handrails of 35–40 mm diameter provide a better grip for both children and adults.